| ARRIS Enterprises, Inc. Confidential Information |
Application Service OverviewThe Application Service is responsible for handling applications in the system. An application is a software module which, in contrast to a service in the platform, is designed to interact with the user. The basic functionality of the Application Service is to facilitate concurrent execution of multiple applications.
OverviewTo manage the behaviours of different types of applications, each application is designated as either primary, secondary or noninteractive. The primary application is the main UI, secondary applications are typically OTT services or similar, and noninteractive applications are auxiliary system applications that may render graphics. For more details, see multiple application terminology. Applications have application properties that convey various pieces of information about the application and its behavior. Properties of secondary applications can be read via the ToiSecondaryApplication.getProperties() function. For information about properties that may be relevant for the portal to take into account, consult the application specific documentation. The process of deciding which application should be visible and receive user input is the responsibility of the user interface, which is implemented in the primary application. The Application Service supplies the interface to implement this functionality. This means that the user interface needs to actively decide which secondary application to make visible and when it should receive input. The primary application is always visible on top of any running secondary applications. This enables functionality in the primary application such as rendering popups or menus on top of other applications. It also means that the primary application needs to make itself transparent in order for any secondary applications to actually become visible to the end user. In a production environment the primary application should always be running. If the primary application crashes, any secondary applications that were visible will be hidden and the primary application will be restarted. Application StatesThe main responsibility of the Application Service is to manage the
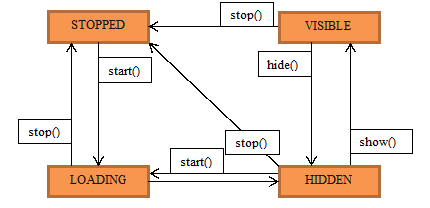
states of the secondary applications. The secondary applications can
be in four different states:
Secondary Application state diagram.
Dealing with state changesChanging the state of a secondary application is an asynchronous operation that takes time to complete and may fail. Therefore it's not advisable to issue a command to a secondary application and then immediately perform some operation that assumes that the state transition has been completed successfully, such as making the portal transparent to show the application beneath it. The recommended way to handle such situations is to provide an
AsyncCallback when calling
functions that lead to a state change in a Sometimes, secondary applications will change states for other reasons
than a function being called on a To detect state changes that didn't originate from the portal, the event listener mechanism can be used. The events include a ToiStateChangeReason which provides information about what kind of circumstance caused the state change to occur. Listening for these events allow a portal to react to events such as crashes, self-initiated exits or similar events.
Starting and restartingWhen If Standby behaviourWhen the STB enters a standby state, any visible secondary applications will
change state and enter either the As a consequence of the above, the primary application regains input
focus and is expected to make the choice to either display graphics and resume
normal operation or explicitly Setting input focusOnly one primary or secondary application can have input focus. As a consequence, setting input focus to a secondary application will remove input focus from whatever application had it previously. Setting input focus to the primary application is done by resetting input focus via the Application Service. Input handlingMaking input focus exclusive to one application is intended to simplify input handling. In order to enable the primary application to retain control when it has lost input focus, it can eavesdrop on predefined inputs via ToiSecondaryApplication.subscribeKey(). Subscribing via subscribeKey() is done for each secondary application and may be done at any time. This relieves the primary application from the need to keep explicit track of which, if any, secondary application currently has input focus. A secondary application cannot have input focus if it is not VISIBLE. A secondary application that has input focus and leaves the VISIBLE state for any reason will automatically relinquish input focus back to the primary application. Playback OwnershipMedia playback requires resources that are very limited, which means that for most configurations only one video tag can be playing content at any one time. For that reason, the concept of playback ownership determines which application is allowed to utilize these resources. The playback owner is determined as follows: If a secondary application is visible, it is the playback owner. Otherwise, the primary application is playback owner. Portal developers should See also: See also: |