| ARRIS Enterprises, Inc. Confidential Information |
Booting with HTTPThe KreaTV HTTP boot protocol contains two steps. During the first step, the STB sends an HTTP GET request to the HTTP server, which responds with an XML manifest file. This manifest file tells the STB what to do during the second step. 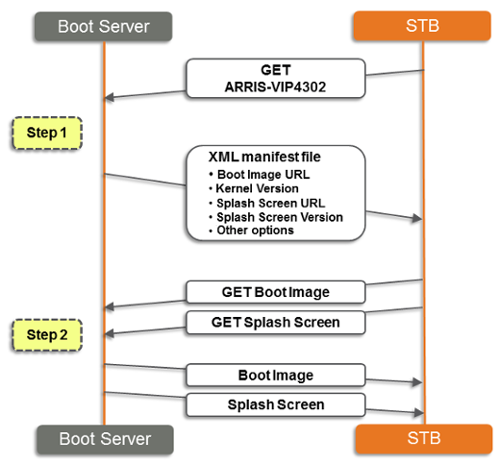
The second step involves reading the manifest file to see which boot server the STB should go to to download the boot image, and what the version of that boot image is. In the simplest case, the HTTP protocol is used again, and the boot image is requested from the same server. But other options exist too. For example, storing the boot images on a different HTTP server. Or if multicast is enabled in the network, the Infocast server could be used to distribute the boot images via multicast. There are several advantages to this two-step process: If the STB has the offered boot image in its flash memory already, no download needs to be performed. Since the STB sends its model and serial number, boot loader version and other details to the server during the first step, the HTTP server can reply with a custom manifest file just for that STB. This is an easy way to allow great flexibility in managing the STB population. By allowing other protocols in the second step, the advantages of multicast neworks (constant bandwidth usage) can be taken advantage of in the distribution of the boot image. Only parts of the HTTP 1.1 specification are implemented, URLs containing non-escaped reserved characters are not supported. Server redirects with code 301, 302 and 303 are supported. |

